InfiniteEARTH and Blue Carbon
What Is
Blue Carbon ?
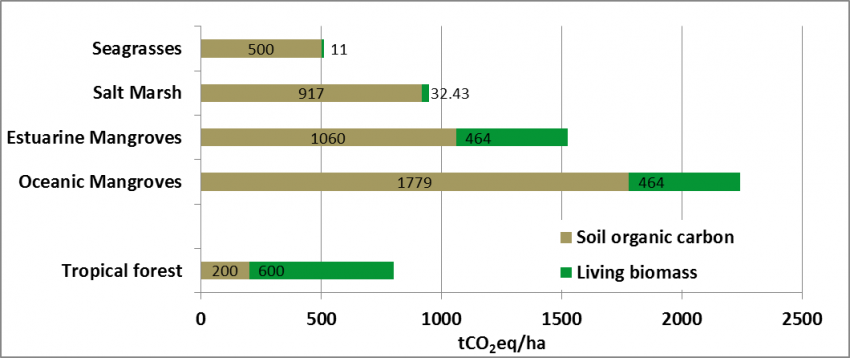
Blue Carbon is essentially carbon captured by the Earth’s oceans and coastal ecosystems. Although smaller in size than our planet’s forests, sea grass, microalgae, mangroves and salt marshes sequester carbon at a much faster rate than their terrestrial counterparts. They have also been acting as carbon sinks for much longer (often millions of years).
Despite covering less than 0.5% ocean’s seabed, the ocean’s vegetated habitats are responsible for more than 50% (and possibly 70%), of all carbon storage in ocean sediments. Mangroves, salt marshes and seagrass make up the majority of the ocean’s vegetated habitats but, while covering less than 0.05% of the plant biomass on land.
As these ecosystems are damaged, due to man-made activities and climate change, they emit enormous amounts of carbon back into our atmosphere – further contributing to the acceleration of climate change and extreme weather events.
Working with of communities and governments to value and conserve their coastal ecosystems is essential to maintaining the long-term mitigation of coastal ecosystems.
One method of slowing climate change impacts is to incorporate coastal wetlands into the carbon market through the buying and selling of carbon offsets. This approach creates a financial incentive for restoration and conservation projects by helping to alleviate federal and state carbon taxes aimed at discouraging the use of fossil fuels.
Alongside tropical forests and peatlands, coastal ecosystems demonstrate how nature can be used to enhance climate change mitigation strategies and therefore offer opportunities for countries to achieve their emissions reduction targets and Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) under the Paris Agreement.
The ongoing destruction and loss of these systems contributes to additional human-induced greenhouse Many countries have included coastal ecosystem management in their national climate change mitigation activities, including under REDD+, NAMAs, NDCs and other mechanisms. InfiniteEARTH’s Rimba Raya Biodiversity Reserve ……


